Physics of capnography
Advances in main-stream sensor technology
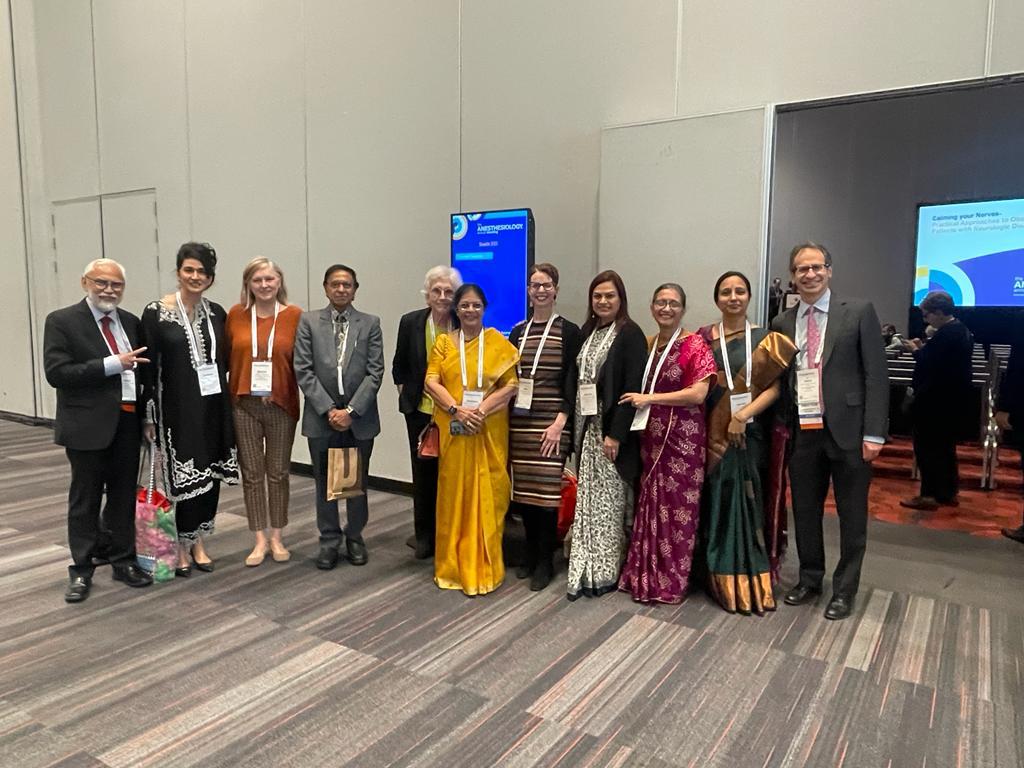
New developments in mainstream sensor technology have overcome many disadvantages associated with earlier models, such as heavy weight, bulky size, facial burns as a result of heated sensors, and increased drag on the endotracheal tubes. In addition, an aspiration sampling pump has been incorporated into the system so that mainstream sensors can function as sidestream sensors in non-intubated patients.
Plug & Play modules.
Respironics has recently released several new versions of the technology. The CAPNOSTAT® 5 is a new solid-state mainstream inspiration, as a sensor that is small and lightweight. It provides a variety of airway adapters to monitor adult, pediatric and neonatal patients.
 |
 |
In addition, they have released LoFlo®, a new Sidestream sensor. The LoFlo technology has a 50cc sampling rate and has a new external sample cell that is attached to the patient interface rather than housed inside the monitor. This design eliminates the need for the respiratory gas sample to be pulled inside the internal infrared measurement bench and eliminates the associated contamination complications as experienced in older sidestream systems. A wide selection of nasal cannulas, traditional, oral and dual O2/inspiration, are available, which allow easy monitoring of non-intubated patients.
The Capnostat 5 and LoFlo sensors utilize the same electronics, which makes them easily interchangeable depending on the type of patient, intubated or non-intubated, you are monitoring.
PHASEIN Medical Technologies, AB, Stockholm, Sweden, introduced the miniaturized mainstream multigas analyzer. The Journal of Clinical Monitoring and Computing (2009; 23(6)355-61) published a performance review of this miniaturized main-stream multigas monitor (MSGM). The unit uses an infrared technique for carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and inhalation agent measurements and a fuel cell technique for breath-to-breath oxygen monitoring. The performance of this analyzer was compared to a side-stream monitor (Datex-Ohmeda S/5® in a bench study. The response time of the MSGM was 2-4 times shorter than that of the side-stream monitor. There was a lower bias regarding CO2 accuracy for the side-stream system. At a high breathing frequency (60BPM) the side-stream system displayed damped O2 and CO2 trace with an amplitude of less than 65% of the main-stream system. Both systems were unaffected by water vapor during a 3-hour test. It would be interesting to compare this system with analyzers using Microstream technology®.

 Twitter
Twitter Youtube
Youtube